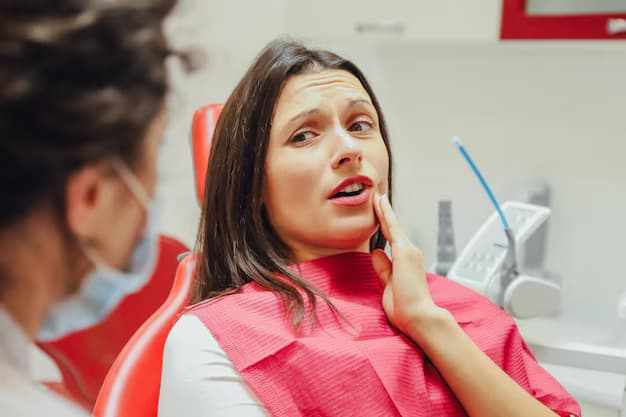
Gum disease is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults and a major contributor to declining oral health when left untreated. Many people search for a dentist for gum disease only after noticeable symptoms appear, yet early care plays a critical role in preventing serious damage. Periodontal health affects not only the gums but also the teeth, jawbone, and overall wellbeing. This guide explains the importance of gum health, how gum disease develops, and why professional treatment is essential for long lasting oral stability.
Understanding Periodontal Health
Periodontal health refers to the condition of the gums and supporting structures that hold the teeth in place. Healthy gums form a tight seal around the teeth and protect underlying bone from infection.
The Role of Gums in Oral Health
Gums act as a barrier against bacteria and debris. They support teeth during chewing and help maintain proper alignment. When gums are healthy, they appear firm and pink and do not bleed easily.
What Happens When Periodontal Health Declines
When bacteria accumulate along the gumline, inflammation develops. Over time, this can damage the connective tissue and bone that support the teeth. Seeking care from a dentist for gum disease helps stop this process before it becomes irreversible.
What Is Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is an infection of the gum tissues caused by bacterial buildup. It progresses gradually and often without pain in the early stages.
Causes of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is plaque buildup. Plaque forms daily and contains harmful bacteria. Without proper brushing and flossing, plaque hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums and allows infection to spread.
Stages of Gum Disease
Gum disease develops in stages. The first stage is gingivitis. At this stage, gums become inflamed but no permanent damage has occurred. The second stage is periodontitis. This stage involves bone loss, deep gum pockets, and a higher risk of tooth loss.
Common Signs You Need a Dentist for Gum Disease
Gum disease often begins with subtle symptoms. Recognizing these warning signs allows for early professional care.
Bleeding Gums
Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing are often inflamed. Consistent bleeding is not normal and may indicate gum disease.
Swollen or Tender Gums
Inflammation causes gums to appear red and swollen. Tenderness may develop as infection progresses.
Persistent Bad Breath
Bacteria trapped beneath the gums can cause ongoing bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth that does not improve with brushing alone.
Gum Recession
When gums pull away from the teeth, roots become exposed. This can lead to sensitivity and an increased risk of decay.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
Advanced gum disease weakens the structures that hold teeth in place. Teeth may feel loose or change position, affecting bite and comfort.
Why Professional Treatment Is Essential
Home care alone cannot reverse moderate or advanced gum disease. A dentist for gum disease provides specialized care that targets infection below the gumline.
Accurate Diagnosis and Assessment
Dental professionals evaluate gum health using measurements, imaging, and visual examination. This allows for precise diagnosis and personalized treatment planning.
Preventing Tooth and Bone Loss
Timely treatment helps stop infection before it causes permanent damage. Professional care preserves natural teeth and maintains jawbone strength.
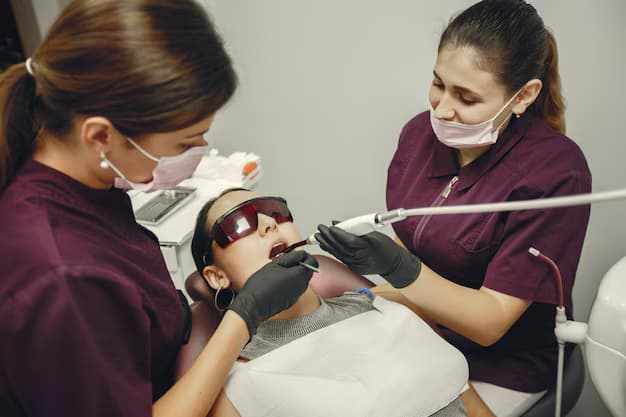
Professional Treatments for Gum Disease
Treatment options depend on the severity of the condition. Early stages respond well to conservative care, while advanced cases require more intensive treatment.
Professional Dental Cleaning
For mild gum disease, professional cleaning removes plaque and tartar from above and just below the gumline. This reduces inflammation and allows gums to heal.
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure used for more advanced gum disease. It removes bacteria from deep pockets and smooths tooth roots to promote reattachment of the gums.
Periodontal Maintenance Care
After initial treatment, ongoing maintenance is essential. Regular cleanings and monitoring help prevent recurrence and control bacteria levels.
Risk Factors That Increase Gum Disease
Certain factors make individuals more susceptible to gum disease. Awareness of these risks supports prevention and early intervention.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco use reduces blood flow to the gums and weakens the immune response. This increases the severity of gum disease and slows healing.
Medical Conditions
Conditions such as diabetes can impair the body’s ability to fight infection. Hormonal changes can also increase gum sensitivity and inflammation.
Genetics
Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to gum disease. Even with good oral hygiene, they may require more frequent professional care.
How Gum Disease Affects Overall Health
Gum disease does not only affect the mouth. Research has shown strong links between periodontal disease and systemic health conditions.
Heart Health and Inflammation
Bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream and contribute to inflammation in blood vessels. This may increase the risk of heart related conditions.
Diabetes and Blood Sugar Control
Gum disease can make blood sugar levels harder to manage. Treating gum disease often improves diabetes control and overall health outcomes.
Respiratory Health Risks
Oral bacteria may be inhaled into the lungs, increasing the risk of respiratory infections, especially in older adults.
Preventing Gum Disease Long Term
Preventive care is the foundation of periodontal health. Daily habits and professional support work together to protect the gums.
Daily Oral Hygiene Practices
Brushing twice daily and flossing regularly help remove plaque before it causes inflammation. Using antibacterial rinses may provide additional protection.
Regular Dental Visits
Routine dental checkups allow early detection of gum disease. Early treatment is often simpler and more effective.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Balanced nutrition, stress management, and avoiding tobacco support a strong immune system and healthier gums.
Living With and Managing Gum Disease
Gum disease is a chronic condition that requires ongoing attention. With proper care, many individuals maintain stable oral health.
Importance of Consistent Care
Following professional recommendations and attending maintenance visits help control gum disease and prevent flare ups.
Monitoring Changes in Gum Health
Paying attention to symptoms such as bleeding or swelling allows for prompt professional care. Early response reduces the risk of complications.
Choosing the Right Dentist for Gum Disease
Selecting a qualified dental professional is essential for effective periodontal care.
Experience in Periodontal Treatment
A dentist for gum disease should have experience diagnosing and managing different stages of periodontal conditions.
Patient Education and Support
Clear explanations and personalized guidance help patients understand their condition and take an active role in their care.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a serious condition that affects the foundation of oral health and can have lasting consequences if left untreated. From early inflammation to advanced bone loss, periodontal disease requires timely and professional care to protect teeth and overall wellbeing. Understanding the signs, risk factors, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their gum health. For those seeking comprehensive periodontal care and ongoing support, Clove Dental Riverpark is dedicated to helping patients achieve healthier gums, stronger teeth, and lasting confidence in their smiles.






Write a comment ...